Measures of Dispersion for Ungrouped Data
We will first choose a suitable class interval for the above data then we will enter the frequency values to complete the table. A measure of dispersion is a quantity that is used to check the variability of data about an average value.

Measures Of Dispersion For Ungrouped Data In Frequency Table Range And Interquartile Range Youtube
What are the Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion.

. SD shortcut method is Assumed Mean formula-Here d is x - A and A is the assumed mean. N being 11 Q 1 is the size of 3rd value. While studying economics students should conduct research use relevant data information and facts and understand the economy of their.
Operations on Sets. It is a method of calculating the central tendency of a scattered dataset. Usually fo r a data set of 100 to 150 observations the.
All of the above answers are correct. 1 2 f f x x s for grouped data. From the table we can observe the number of times the data appears in the data using frequency.
The range is the difference between higher and lower values of the given data. Graphs of Motion. Range variance and standard deviation.
It measures the absolute variability of a distribution. Mean median and mode. The table helps measures the dispersion ie.
SD is the positive square root of variance. Hence standard deviation is an important tool used by statisticians to measure how far or how close are the points in a data group from. Frequency is nothing but the number of times an event occurs in a given scenario.
Quartile deviation is one of the measures of dispersionBefore getting into a deeper understanding lets recall quartiles and how we can define them. A Right Skewed B Left Skewed C Symmetric D bimodal Q5. How many complete dinners can be created from a menu with 3 appetizers 5 soft drinks and 4 desserts if a complete dinner consists of one appetizer one soft drink and one dessert.
We can find the mode by counting the number of times each value occurs in a data set. The mode is the number that appears most frequently in a set of data. Standard Deviation simply stated is the measure of the dispersion of a group of data from its meanIn other words it measures how much the observations differ from the central mean.
A 12 B 60 C 17280 D 30 Q4. Standard Deviation is the measure of the dispersion of data from its mean. 41 58 41 54 49 46 52 53 55 52.
1st Term Test. Sk b Bowleys coefficient of skewness sk b 3 1 3 2 2 1 Q Q Measures of skew ness sk p Pearsons coefficient of skewness sk p S dard Deviation Mean Mode tan Measures of skew ness SS x Sum of Squares SS x 2 x for ungrouped data. Ungrouped data Example 1 Calculate range and QD.
Measures Of Dispersion. Measures of central tendency and dispersion. On the other hand if data consists of individual data points it is called ungrouped data.
Mean deviation variance and standard deviation of ungroupedgrouped data coefficient of variation analysis of frequency distributions with equal means but different variances. Calculation of mean median and mode of grouped and ungrouped data calculation of standard deviation variance and mean deviation for grouped and ungrouped data. Data can be of two types - grouped and ungrouped.
The grouped data computations are used only when a population is being analyzed d. It is the average of all the values given in a set of data. The grouped data result is more accurate than the ungrouped result c.
20 25 29 30 35 39 41. Standard Deviation measures the variability or dispersion of the data. Median is the most middle value in a set of.
The higher is the dispersion or variability of data the larger will be. The measure of dispersion that is influenced most by extreme values is. If the mean of data greater than the median then the data is.
Of the following observations. When data is expressed in the form of class intervals it is known as grouped data. None of the above answers is correct.
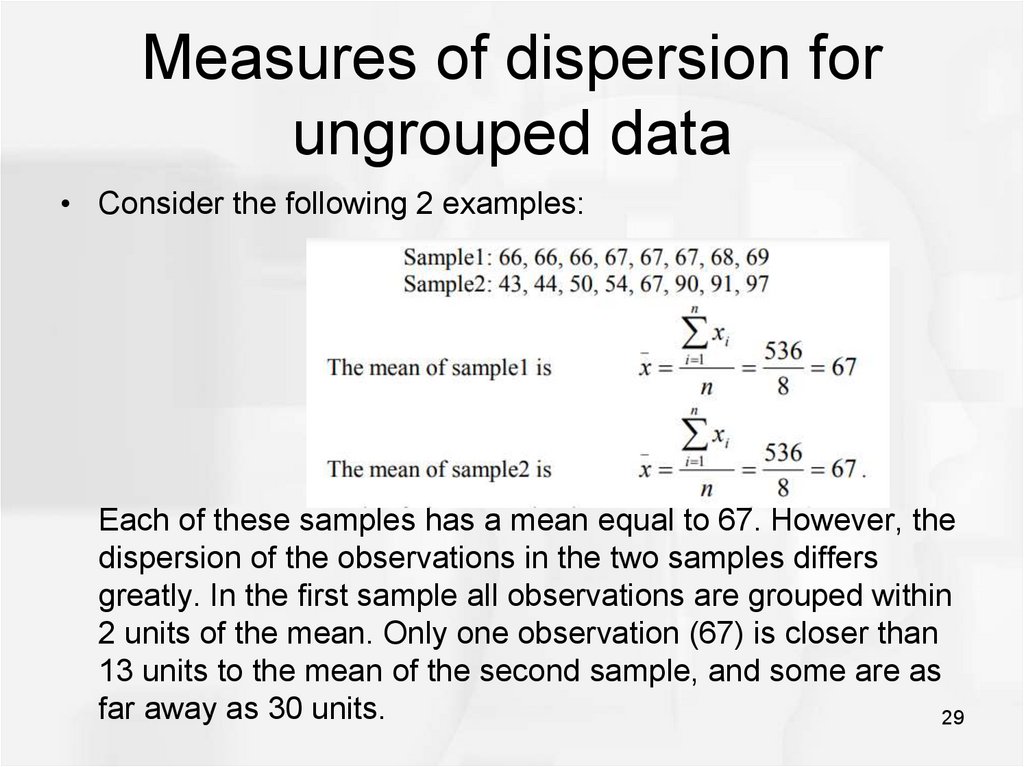
Linear Inequalities in Two Variables. MEASURES OF DISPERSION 77 Q 1 is the size of n1 th 4 value. Measures of Dispersion for Ungrouped Data.
SS f x 2 x for grouped data. Network in Graph Theory. Standard Deviation For Grouped Data.
Measures of central tendency and location ie. Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis With Exercises Solutions and Applications in R By Christian Heumann Michael Schomaker Shalabh. In our example the range of the data is 388.
Lets look at how to determine the Standard Deviation of grouped and ungrouped data as well as the random variables Standard Deviation. As the values are already arranged in ascending order it can be seen that Q 1 the 3rd value is 29. Quartiles are the values that divide a list of numerical data into three-quarters such as Q 1 Q 2 and Q 3The middle part of the three quarters measures the central point of distribution and shows the data values near the.
Use the data to make a frequency table. Number chosen ranges fro m abo ut 5 to 10. So you have to first calculate variance to find SD.
Introduction To Statistics Online Presentation

Department Of Quantitative Methods Information Systems Introduction To

Measures Of Dispersion Of Ungrouped Data

教学为先教育中心 Measures Of Dispersion For Ungrouped Data In Frequency Table Range And Interquartile Range Https Youtu Be Khviwqg 0p0 Facebook
0 Response to "Measures of Dispersion for Ungrouped Data"
Post a Comment